Hair loss, medically known as alopecia, is a common condition that affects millions of individuals worldwide. Whether it’s thinning hair or bald patches, alopecia can have a significant impact on self-esteem and quality of life. If you’re experiencing hair loss, you’re not alone. This comprehensive guide aims to provide valuable insights into alopecia by exploring its symptoms, causes, and the latest treatment options available.
Understanding Alopecia
Alopecia is a broad term that encompasses various types of hair loss, each with its own set of symptoms and underlying causes. The most common types of alopecia include:
- Androgenetic Alopecia: Also known as male-pattern baldness or female-pattern baldness, this type of alopecia is characterized by a gradual thinning of hair, typically starting at the crown or temples in men and resulting in a receding hairline or bald spots. In women, it often leads to overall thinning of the hair.
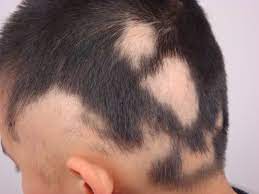
- Alopecia Areata: This autoimmune disorder causes sudden hair loss in small, round patches on the scalp or other parts of the body. It can occur at any age and may result in complete baldness in severe cases.
- Telogen Effluvium: This type of hair loss occurs when a significant number of hair follicles enter the resting phase (telogen) prematurely, leading to excessive shedding and thinning of the hair. It can be triggered by factors such as stress, hormonal changes, illness, or certain medications.
- Traction Alopecia: Caused by excessive pulling or tension on the hair follicles, traction alopecia often results from tight hairstyles such as braids, ponytails, or extensions. Over time, this constant tension can damage the follicles and lead to hair loss.
Exploring the Causes
Understanding the underlying causes of alopecia is crucial for effectively managing and treating the condition. While the exact cause may vary depending on the type of alopecia, several factors can contribute to hair loss:
- Genetic Predisposition: Androgenetic alopecia, the most common type of hair loss, is often hereditary. Individuals with a family history of baldness are more likely to experience hair thinning or baldness themselves.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, such as those occurring during puberty, pregnancy, childbirth, or menopause, can disrupt the hair growth cycle and lead to temporary or permanent hair loss.
- Autoimmune Disorders: Alopecia areata is believed to be an autoimmune condition in which the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the hair follicles, resulting in hair loss.
- Stress and Trauma: Physical or emotional stress can trigger telogen effluvium, causing hair follicles to enter the resting phase prematurely and leading to excessive shedding.
- Scalp Infections: Fungal infections, such as ringworm, can cause inflammation and hair loss if left untreated. Proper hygiene and timely treatment are essential for preventing further hair loss.
Treatment Options:
While there is no one-size-fits-all solution for alopecia, several treatment options are available to help manage and, in some cases, reverse hair loss. The choice of treatment depends on the type and severity of alopecia, as well as individual preferences and medical history. Some common treatment options include:
- Topical Medications: Over-the-counter and prescription topical treatments, such as minoxidil (Rogaine), can help stimulate hair growth and slow down further hair loss. These medications are typically applied directly to the scalp once or twice daily.
- Oral Medications: Finasteride (Propecia) is an oral medication approved for the treatment of androgenetic alopecia in men. It works by inhibiting the conversion of testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone associated with hair loss.
- Corticosteroid Injections: For individuals with alopecia areata, corticosteroid injections directly into the affected areas of the scalp can help suppress the immune response and promote hair regrowth.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: PRP therapy involves injecting the patient’s own platelet-rich plasma into the scalp to stimulate hair follicles and promote hair growth. It’s often used as a complementary treatment for various types of alopecia.
- Hair Transplant Surgery: In cases of advanced hair loss, hair transplant surgery may be recommended to restore a fuller, more natural-looking hairline. Techniques such as micro-sapphire DHI (Direct Hair Implantation) offer precise, minimally invasive procedures with excellent results.
Living with alopecia can be challenging, but understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options available can empower individuals to take control of their hair loss journey. Whether it’s seeking medical advice, exploring different treatment modalities, or embracing one’s unique beauty, there are numerous ways to address alopecia and restore confidence. By staying informed and proactive, individuals can navigate the complexities of alopecia with resilience and optimism. Remember, you’re not defined by your hair – true beauty comes from within.
Practical Tips for Managing Alopecia
In addition to seeking medical treatment, there are several practical strategies individuals with alopecia can implement to manage their condition and promote overall scalp health:
- Practice Good Hair Care: Gently wash and condition your hair regularly using mild, sulfate-free products suitable for your hair type. Avoid harsh chemicals, excessive heat styling, and tight hairstyles that can cause further damage to the hair follicles.
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Maintain a balanced diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and essential nutrients to support healthy hair growth. Include plenty of protein, iron, omega-3 fatty acids, and antioxidants in your diet by consuming a variety of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains.
- Manage Stress: Chronic stress can exacerbate hair loss and interfere with the hair growth cycle. Practice stress-reducing techniques such as mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, or regular physical activity to promote relaxation and emotional well-being.
- Protect Your Scalp: Shield your scalp from harmful UV rays by wearing a wide-brimmed hat or using a sunscreen specifically formulated for the scalp. Minimize exposure to environmental pollutants and toxins that can damage the hair follicles and contribute to hair loss.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink an adequate amount of water each day to keep your body and scalp hydrated. Proper hydration is essential for maintaining healthy hair and scalp function, as dehydration can lead to dryness, itching, and flakiness.
Alopecia is a complex and multifaceted condition that can have a significant impact on an individual’s physical appearance, emotional well-being, and overall quality of life. By understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options available, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their hair loss journey effectively. Whether it’s seeking medical advice, exploring different treatment modalities, or implementing practical strategies for scalp care, there are numerous ways to address alopecia and regain confidence. Remember, you’re not defined by your hair – true beauty comes from within. Embrace your unique journey, celebrate your strengths, and surround yourself with love and support. With the right mindset and resources, individuals with alopecia can navigate the challenges of hair loss with resilience, courage, and dignity.


